Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the gradual decline in cognitive functions, memory, and reasoning abilities. Understanding its intricacies can help in recognizing early symptoms and managing the condition effectively. Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia among older adults, accounting for 60-80% of cases. The disease results from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Key symptoms include memory loss, confusion, difficulty in performing familiar tasks, and changes in personality and behavior. As the disease progresses, these symptoms become more severe, impacting the individual’s ability to carry out daily activities.
Research indicates that the buildup of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain are significant contributors to Alzheimer’s. These abnormal structures damage and kill nerve cells, leading to the symptoms associated with the disease. While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, early diagnosis and intervention can help slow its progression and improve the quality of life for those affected. Understanding the disease’s mechanisms and risk factors is crucial for developing preventive strategies and effective treatments.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is vital for managing its progression and improving patient outcomes. Identifying the condition at an early stage allows for timely intervention, which can help slow the disease’s advancement and enhance the quality of life. Early detection involves recognizing subtle changes in memory and cognitive abilities that may indicate the onset of Alzheimer’s. Regular medical check-ups and cognitive assessments can aid in spotting these early signs.
Family members and caregivers play a crucial role in early detection by observing changes in behavior and cognitive function. Early diagnosis also opens up opportunities for participating in clinical trials and accessing emerging treatments that may not be available to those diagnosed at later stages. It enables individuals and families to plan for the future, making informed decisions about care, finances, and legal matters. Furthermore, early detection can alleviate anxiety by providing clarity and direction for managing the condition.
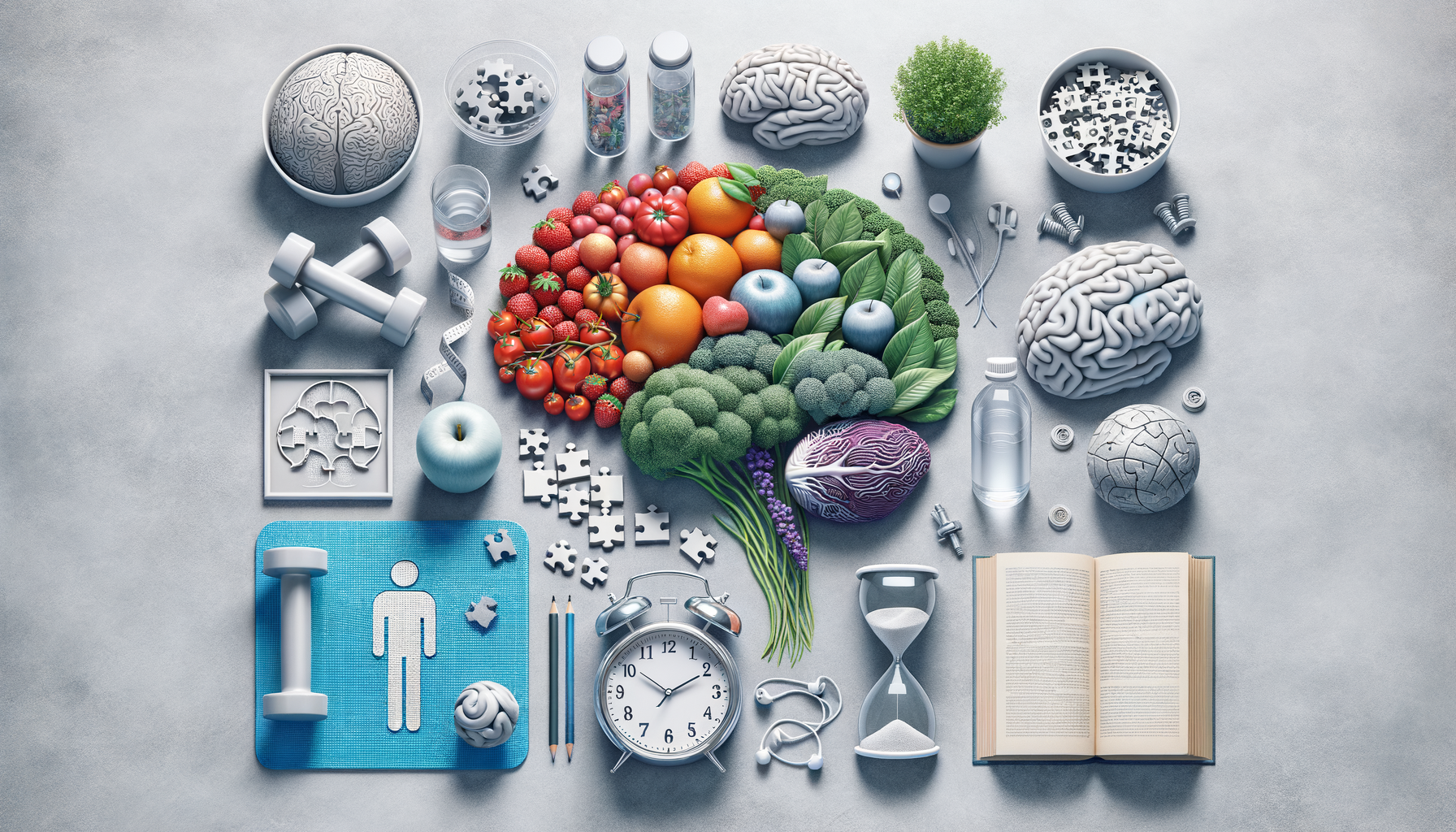
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Research suggests that certain lifestyle modifications can help maintain brain health and prevent cognitive decline. These include:
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, which provides essential nutrients for brain health.
- Regular physical activity, which improves blood flow to the brain and promotes the growth of new brain cells.
- Mental stimulation through activities like reading, puzzles, and learning new skills, which can enhance cognitive reserve.
- Social engagement, as maintaining strong social connections can support cognitive health and reduce the risk of dementia.
- Quality sleep, as poor sleep patterns are linked to increased amyloid plaque accumulation in the brain.
These lifestyle changes not only contribute to overall health but also create a protective barrier against Alzheimer’s. While genetic factors cannot be changed, lifestyle choices are within our control and can make a significant difference in reducing the risk of this disease.
Role of Nutrition in Brain Health
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining brain health and preventing Alzheimer’s disease. A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins and minerals can support cognitive function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases. The Mediterranean diet, for example, has been associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s due to its emphasis on plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
Key nutrients that support brain health include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which have anti-inflammatory properties and support neuronal function.
- Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, which help combat oxidative stress and protect brain cells from damage.
- B vitamins, including B6, B12, and folate, which are essential for brain function and may reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Incorporating these nutrients into the diet can help maintain cognitive health and potentially delay the onset of Alzheimer’s symptoms. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized dietary recommendations and to ensure that nutritional needs are met.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s disease poses a significant challenge to individuals and families worldwide. However, by understanding the disease, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting preventive strategies, it is possible to reduce the risk and manage its impact effectively. Lifestyle modifications, early detection, and proper nutrition play crucial roles in maintaining brain health and delaying the progression of Alzheimer’s.
Taking proactive steps today can lead to a healthier future, with a focus on preserving cognitive function and enhancing quality of life. While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, ongoing research and advancements in treatment offer hope for better management and potential breakthroughs in the future. By staying informed and engaged, individuals can take control of their brain health and contribute to a world where Alzheimer’s is less prevalent.


Leave a Reply