Introduction to Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by itchy, red, and swollen skin, it significantly impacts the quality of life for those affected. The condition is often associated with other atopic disorders such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. Understanding the mechanisms and treatment options for atopic dermatitis is crucial for effective management and improving patient outcomes.
The Role of the Immune System in Atopic Dermatitis
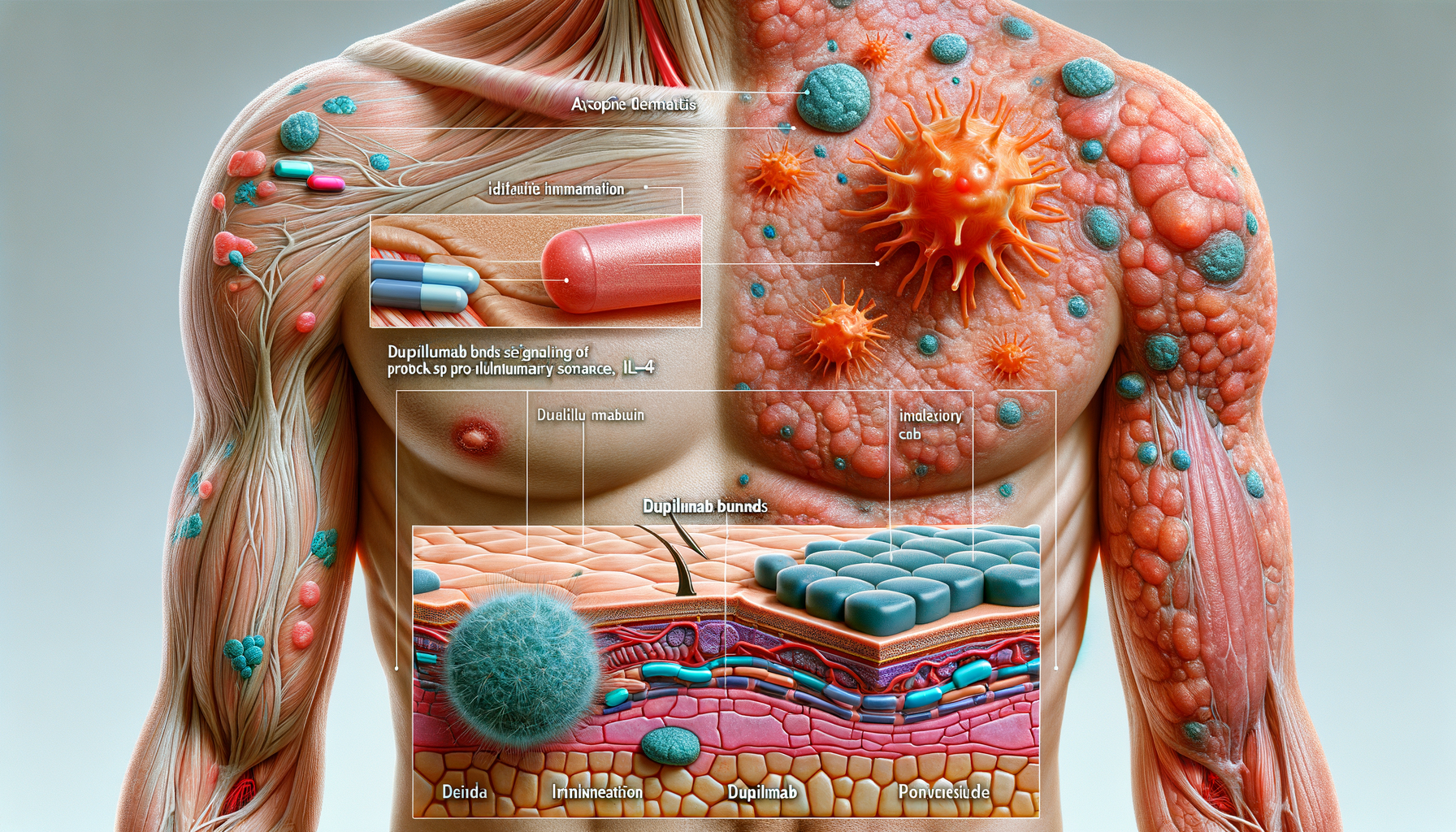
Atopic dermatitis is primarily driven by an overactive immune response. The skin’s barrier function is compromised, allowing allergens and irritants to penetrate and trigger an immune reaction. This leads to the release of inflammatory cytokines, which exacerbate skin inflammation. The immune system’s involvement is a key factor in the chronic nature of the disease, necessitating treatments that target these immune pathways.
- Increased levels of cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13 are observed in affected individuals.
- These cytokines play a significant role in the inflammatory process and skin barrier dysfunction.
- Understanding this immune response is vital for developing targeted therapies.
Introduction to Dupilumab
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that has emerged as a promising treatment for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. It works by inhibiting the signaling of IL-4 and IL-13, the cytokines implicated in the inflammatory process of the disease. By targeting these pathways, Dupilumab effectively reduces inflammation and improves skin barrier function, offering relief to patients who have not responded to conventional therapies.
- Dupilumab is administered via subcutaneous injection, typically every two weeks.
- Clinical trials have shown significant improvement in skin clearance and reduction in itch.
- The treatment is generally well-tolerated, with few side effects.
Effectiveness and Clinical Outcomes of Dupilumab
The effectiveness of Dupilumab has been demonstrated in numerous clinical trials. Patients receiving Dupilumab have shown marked improvement in skin lesions and a reduction in the severity of itching. These outcomes contribute to enhanced quality of life and reduced psychological distress associated with the condition. Furthermore, Dupilumab has been associated with fewer flare-ups and longer periods of remission.
- Studies report a significant decrease in eczema area and severity index (EASI) scores.
- Patients experience rapid relief from itching, often within the first week of treatment.
- Long-term use of Dupilumab is linked to sustained improvements in skin condition.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Dupilumab represents a significant advancement in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, offering hope to those with moderate-to-severe forms of the condition. Its ability to target specific immune pathways makes it a powerful option in the therapeutic arsenal. As research continues, there is potential for further refinement of treatments and the development of additional biologics that can provide even greater benefits to patients. For individuals managing atopic dermatitis, staying informed about emerging therapies is essential to finding effective solutions and improving their quality of life.



Leave a Reply