Precision Eyebrow Trimmer | Safe Hair Removal for Women
The Evolution of Eyebrow Grooming
Eyebrow grooming has morphed from a simple beauty routine into an art form, reflecting personal style and cultural trends. Historically, eyebrows have been shaped and styled using various methods ranging from tweezers to threading. However, the introduction of the eyebrow trimmer has revolutionized this aspect of beauty care. This tool provides precision and ease, allowing individuals to maintain their eyebrows at home without the need for professional services. The rise of the eyebrow trimmer can be attributed to its efficiency and the clean results it delivers, making it a popular choice for those seeking a quick and safe hair removal solution.
Understanding the Precision Eyebrow Trimmer
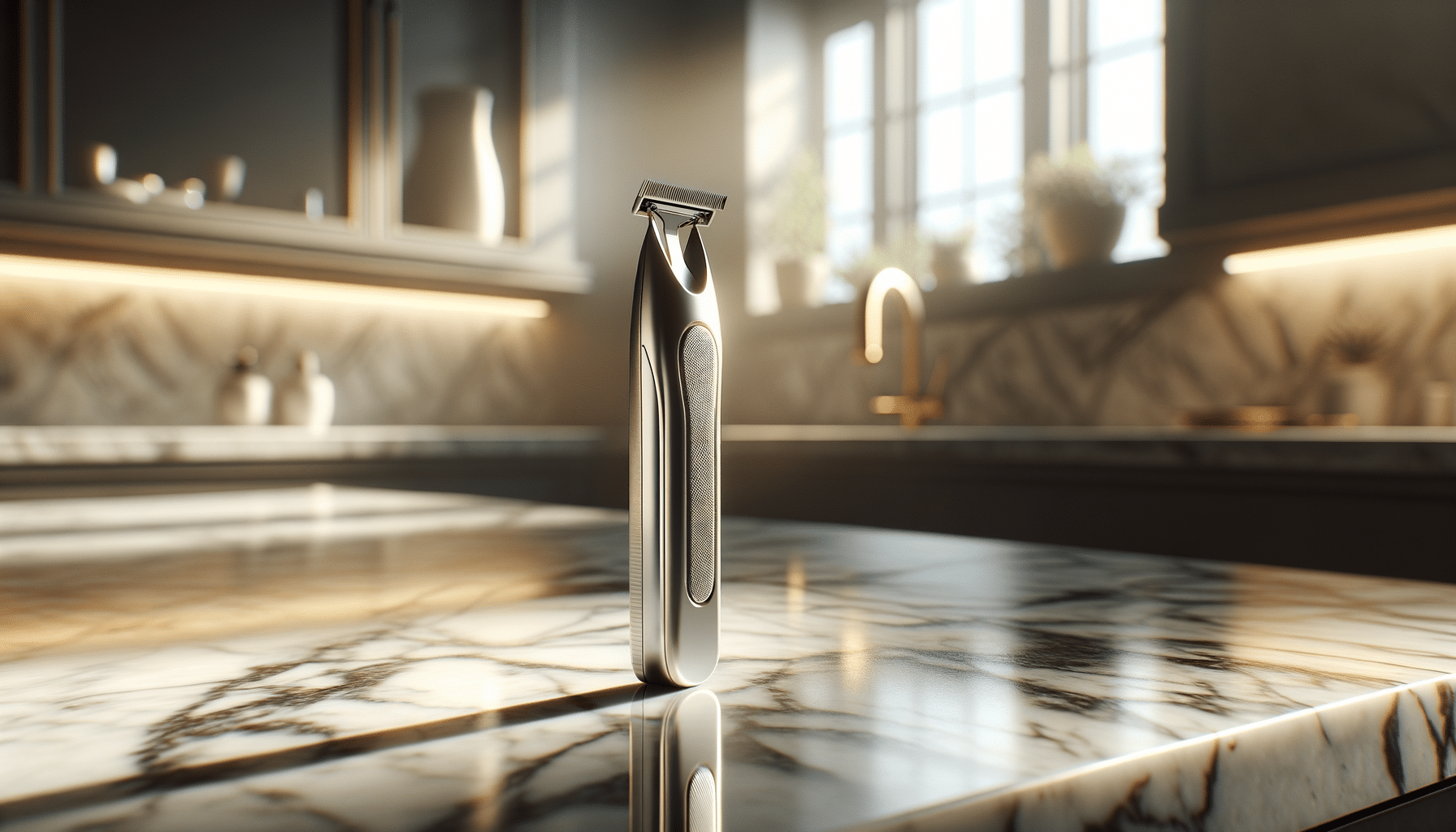
A precision eyebrow trimmer is designed specifically for the delicate task of shaping eyebrows. Unlike traditional methods, such as waxing or plucking, which can be painful and time-consuming, a trimmer offers a painless experience. It typically features a small, angled blade that allows for detailed trimming, ensuring each hair is cut to the desired length without pulling or tugging. This tool is ideal for creating clean lines and defining the shape of the brows. The precision offered by these trimmers ensures that users can achieve their desired look with minimal effort and maximum safety.
Advantages of Using an Eyebrow Trimmer
Using an eyebrow trimmer comes with several advantages, making it a preferred choice for many. Firstly, it offers a pain-free grooming experience, which is a significant benefit for those with sensitive skin. Secondly, the trimmer provides precise control, allowing users to shape their eyebrows with accuracy. This precision is particularly useful for achieving symmetrical brows, which can be challenging with other methods. Additionally, eyebrow trimmers are portable and easy to use, making them convenient for quick touch-ups. They are also a hygienic option as they reduce the risk of skin irritation and ingrown hairs.
- Pain-free grooming
- Precision and control
- Convenient and portable
- Reduces skin irritation
Choosing the Right Eyebrow Trimmer
When selecting an eyebrow trimmer, several factors should be considered to ensure it meets your grooming needs. It’s important to look for a trimmer with a sharp, stainless steel blade for clean results. Battery-operated models are often more convenient, providing flexibility without the restriction of cords. Additional features such as adjustable combs can enhance the trimming experience by allowing customization of the eyebrow length. Reading user reviews and ratings can also provide insight into the trimmer’s performance and durability. Ultimately, choosing a high-quality trimmer can make a significant difference in the ease and effectiveness of your eyebrow grooming routine.
Conclusion: Achieving Flawless Brows with Ease
The precision eyebrow trimmer is a game-changer in the realm of personal grooming. Its ability to deliver clean, safe, and painless results makes it an essential tool for anyone looking to maintain well-shaped eyebrows. As grooming trends continue to evolve, the eyebrow trimmer stands out as a reliable and efficient solution. For those seeking a quick and safe hair removal option, this tool offers a convenient alternative to traditional methods, ensuring that your eyebrows always look their best with minimal effort.