Why These Everyday Foods Might Be Making Your Gout Worse
Understanding Gout and Its Triggers
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes severe pain, swelling, and redness in the joints. It occurs when uric acid builds up in the blood, leading to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints. Understanding what triggers gout is crucial for managing this condition. One of the key factors in managing gout is diet. Certain foods can increase uric acid levels, making gout symptoms worse. To effectively manage gout, it is important to identify and avoid these dietary triggers.
Uric acid is a waste product formed from the breakdown of purines, which are found in many foods. When the body produces too much uric acid or fails to excrete it efficiently, it can lead to gout attacks. Foods high in purines can exacerbate this condition, making dietary choices a critical aspect of gout management.
While genetics and other health conditions can contribute to gout, diet remains a significant factor. By understanding the role of certain foods in triggering gout, individuals can make informed dietary choices to minimize flare-ups and manage their condition more effectively.
High-Purine Foods to Avoid
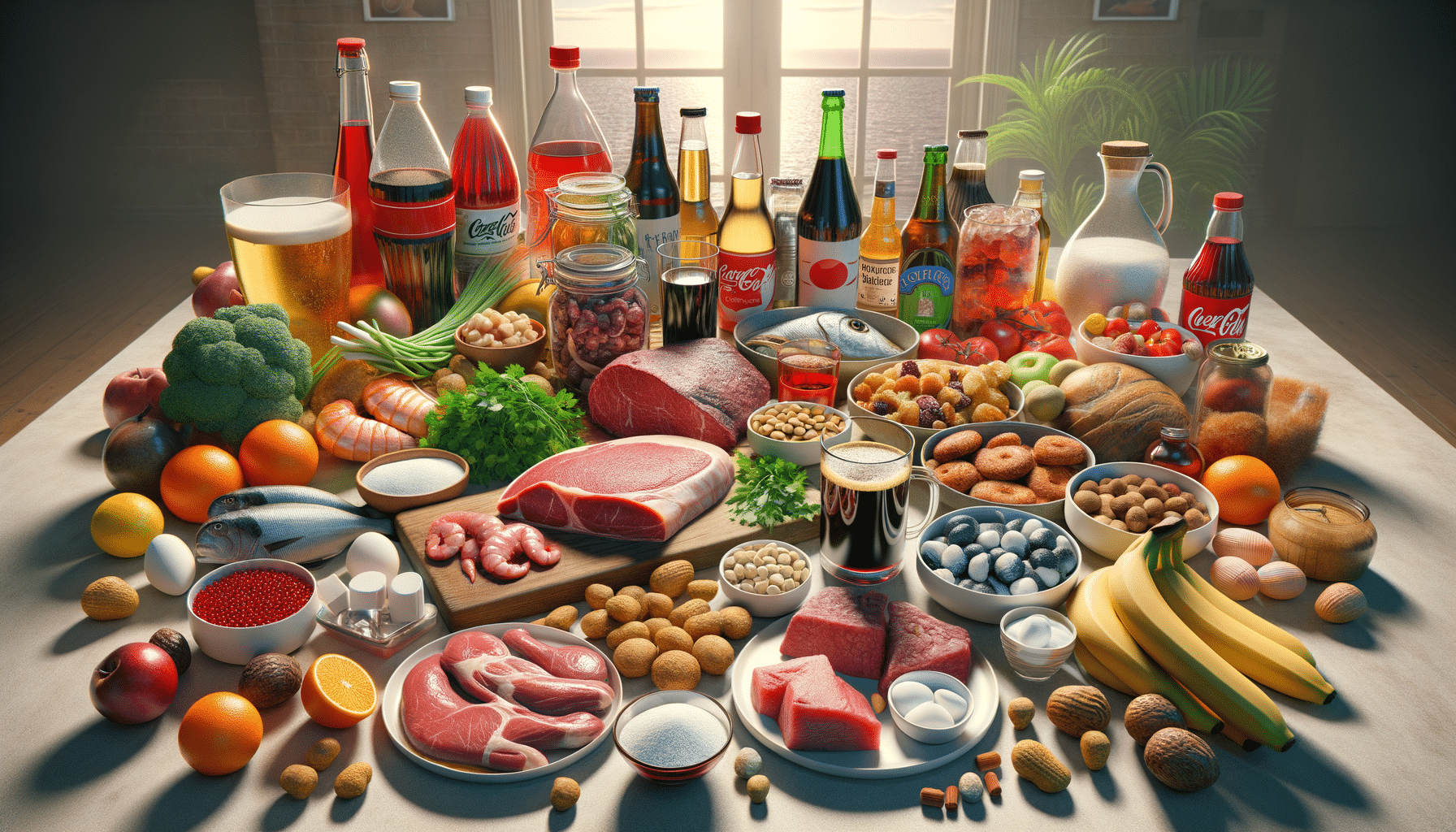
One of the primary dietary considerations for managing gout is reducing the intake of high-purine foods. Purines are naturally occurring substances found in certain foods, and their breakdown leads to the production of uric acid. When consumed in large amounts, high-purine foods can significantly increase uric acid levels, triggering gout attacks.
Some common high-purine foods include:
- Organ meats such as liver and kidneys
- Red meats like beef and lamb
- Seafood, especially shellfish like shrimp and lobster
- Certain fish, including sardines and mackerel
These foods contain high levels of purines and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether by individuals prone to gout. Instead, opting for low-purine alternatives can help manage uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout flare-ups.
By being mindful of purine-rich foods and making conscious dietary choices, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their gout and improving their overall health.
The Impact of Alcohol and Sugary Beverages
Alcohol and sugary beverages are often overlooked as dietary triggers for gout, but they can have a significant impact on uric acid levels. Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, is known to increase uric acid production and decrease its excretion, leading to an elevated risk of gout attacks.
Sugary beverages, including sodas and fruit juices, can also contribute to gout. These drinks often contain high levels of fructose, a type of sugar that can increase uric acid production. Studies have shown that excessive consumption of fructose-rich beverages is associated with a higher risk of developing gout.
For individuals with gout, limiting or avoiding alcohol and sugary drinks is an important step in managing their condition. Instead, opting for water, herbal teas, or low-sugar alternatives can help maintain healthy uric acid levels and reduce the frequency of gout flare-ups.
By making mindful beverage choices, individuals can support their overall health and minimize the impact of gout on their daily lives.
Exploring Low-Purine Alternatives
Adopting a low-purine diet is a practical approach to managing gout. By choosing foods that are naturally low in purines, individuals can help control their uric acid levels and reduce the likelihood of gout attacks.
Some low-purine food options include:
- Fruits such as cherries, apples, and berries
- Vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and kale
- Whole grains, including oats and brown rice
- Lean proteins such as chicken and tofu
These foods not only help manage gout but also provide essential nutrients that support overall health. Incorporating a variety of low-purine foods into the diet can enhance nutrition while minimizing the risk of gout flare-ups.
By embracing a balanced diet rich in low-purine foods, individuals can take control of their gout and enjoy a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Gout Through Diet
Managing gout effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary modifications. By understanding the impact of certain foods on uric acid levels, individuals can make informed choices to minimize their risk of gout attacks.
Reducing the intake of high-purine foods, limiting alcohol and sugary beverages, and embracing low-purine alternatives are key strategies in managing gout. These dietary adjustments, combined with medical guidance, can help individuals lead a more comfortable and active life despite their condition.
Ultimately, taking control of gout through diet empowers individuals to improve their quality of life and reduce the burden of this painful condition.